The temporomandibular joint and its disorders
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is possibly one of the most interesting joints in the human body. It is an essential part of the masticatory system and it joins the cranium and the mandible, playing an important role in growth and adaptation. This joint is unique in that it is a bilateral joint that functions as one unit; the two sides are joined together by the mandibular bone and connected to the temporal bone of the skull on each side. Both sides can have different functional movements, one from the other, but with a certain degree of correlation.
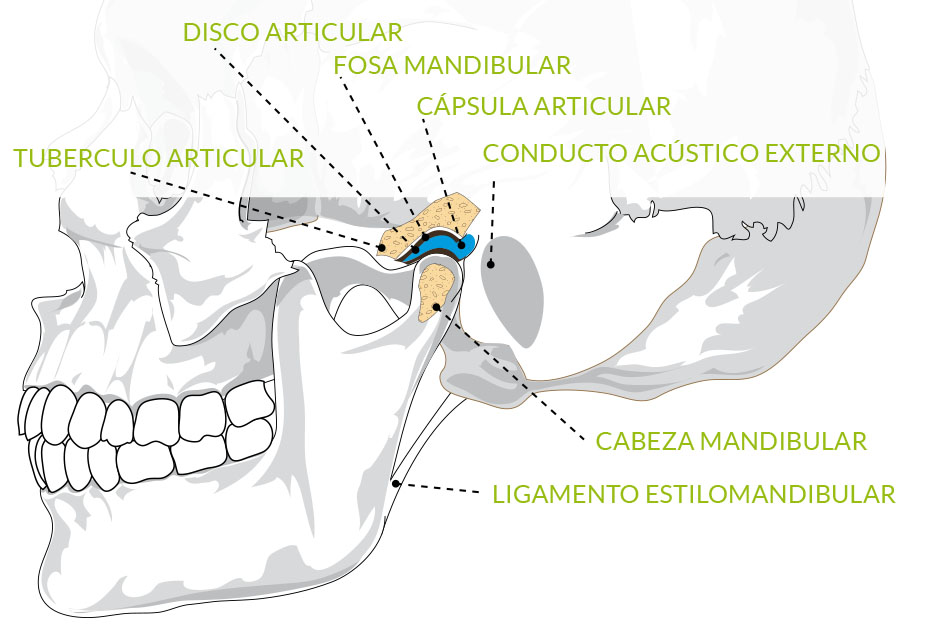
The TMJ involves the articular surfaces, the articular discs and the joining elements (muscle and ligament system). It is a group of bones, muscles, ligaments and other structures that coordinate uni or bilaterally to develop their function and to maintain the equilibrium of the joint. The condylar disc divides the TMJ in two subjoints, upper (disc-temporal bone) and lower (disc-condyle).
The articular disc is one of the most complex elements when assessing the TMJ. It is often partially or totally dislocated either temporarily or permanently, which can cause degeneration and severe pain or dysfunction. There is still a lot to discover regarding this dislocation
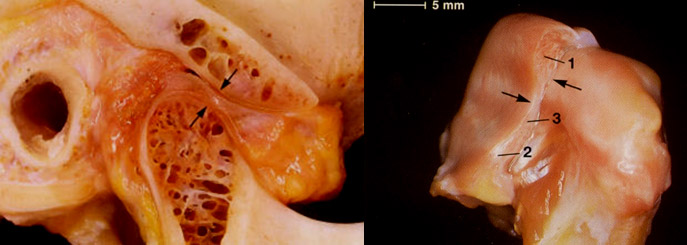
Images taken from Bumann, A, Lotzmann, U. Análisis instrumental de los movimientos, In: Bumann, A, Lotzmann U, editores. Atlas de diagnóstico funcional y principios terapéuticos en odontología. 1ed. Barcelona: Masson; 2000.
The cause and mechanism behind the TMJ disorders is still unsolved, and there are different theories that try to explain the clinical symptoms. The main theories are mechanic, psycho-physiological, myogenic and multifactorial (currently the one with most followers).
According to Okeson, the normal function of the masticatory system can be affected by certain events (local and systemic factors) that will affect it directly, but it is the individual´s physiological tolerance that will lead or not to the appearance of symptoms.
The most common treatment for this type of disorders range from gentle occlusal adjustment, occlusal splints to stabilize the joint, physiotherapy, pharmacological treatment prescribed either by the dentist or the neurologist, physiological therapy for stressful or anxiety disorders and, in the most severe cases, surgery (such as arthrocentesis).
RELATED TREATMENTS
In Clínica Dental Avante all of our specialist dentists work together and can carry out any additional treatment that is required, related or not to endodontic treatments.